Study of direct photon production in Pb-Pb collisions at √sNN = 5.02 TeV with ALICE experiment’s Photon Spectrometer (PHOS) at Large Hadron Collider
room 207, Pasteura 7 / https://www.gotomeet.me/NCBJmeetings/phd-seminar / https://events.ncbj.gov.pl/e/Seminar_23_24
09 May, 2024 - 09 May, 2024

The Transient Southern Sky
ul. Pasteura 7, sala 404 / https://www.gotomeet.me/NCBJmeetings/seminarium-astrofizyczne
30 Apr, 2024 - 30 Apr, 2024

Badanie egzotycznych nuklidów metodą masowej separacji on-line
PNT (sala Maria)
07 May, 2024 - 07 May, 2024

Future Opportunities of Lignin derived Advanced Materials
https://meet.goto.com/NCBJmeetings/nomaten-seminar
30 Apr, 2024 - 30 Apr, 2024
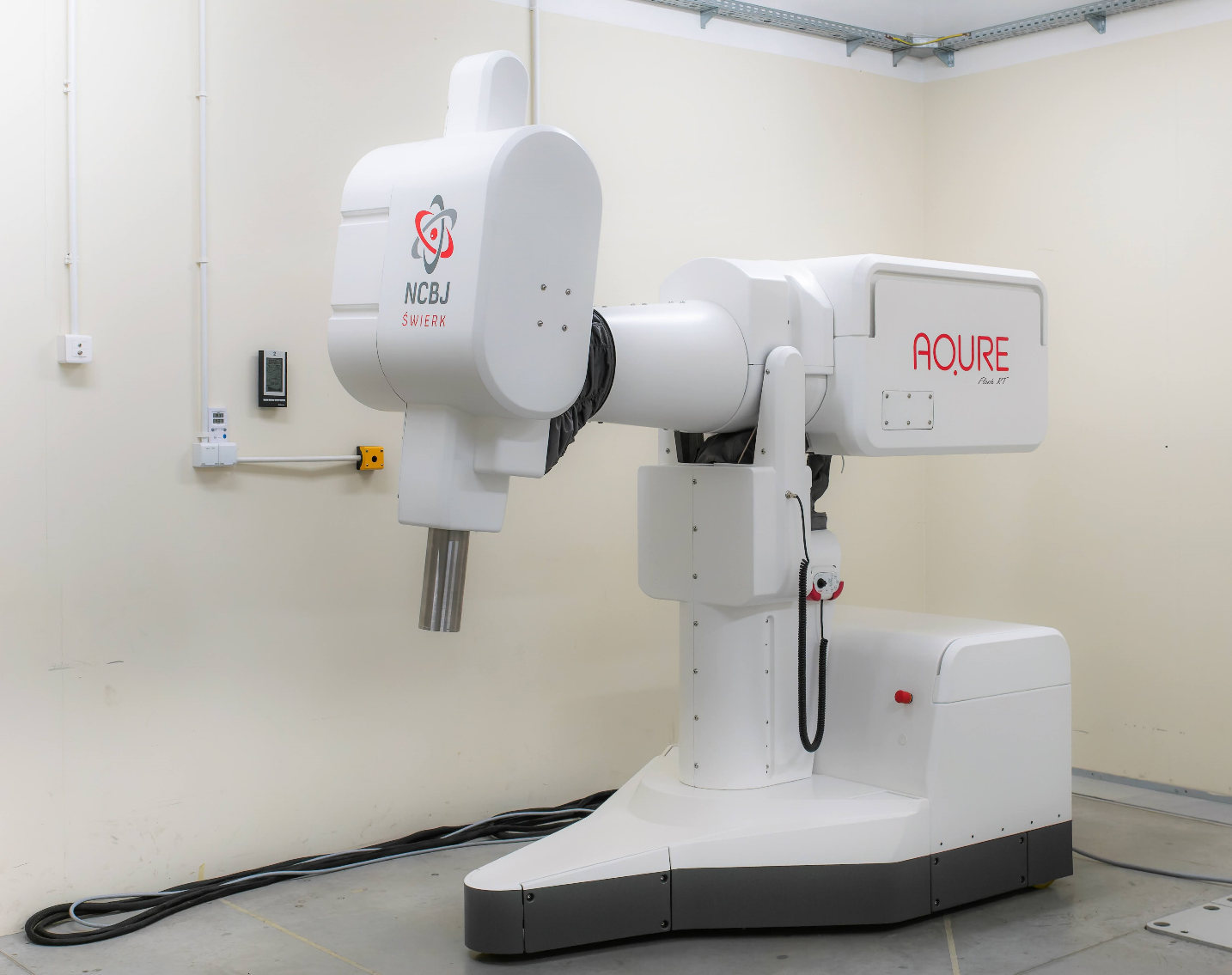

Accelerator in search of new cancer therapies
24-04-2024
27
Apr
2024
Professor | BP2
Deadline: 17-05-2024

Exploring the Low Surface Brightness Galaxies in Abell 194 with Transfer Learning
room 207, Pasteura 7 / https://www.gotomeet.me/NCBJmeetings/phd-seminar / https://events.ncbj.gov.pl/e/Seminar_23_24
25 Apr, 2024 - 25 Apr, 2024

Konkurs MAPS - wielostronna współpraca badawcza pomiędzy Bułgarią, Chorwacją, Węgrami, Polską, Rumunią i Szwajcarią
Finansowanie: Inne
14 Apr, 2024 - 01 Jul, 2024

Can dust evaporate in harsh interstellar environments?
24-04-2024

Dwarf galaxies in deep-wide surveys: a new frontier in the study of galaxy evolution
ul. Pasteura 7, sala 404 / https://meet.goto.com/NCBJmeetings/seminarium-astrofizyczne
23 Apr, 2024 - 23 Apr, 2024




